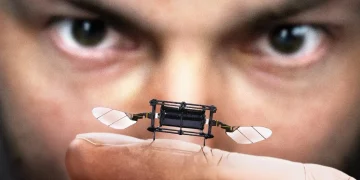
The world of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) is undergoing a transformation, and at the heart of this revolution is an unassuming yet powerful component: miniature gears. These tiny, intricate mechanical elements have the potential to drastically change the way machines are built, how they operate, and how they interact with humans. While gears may seem like an old-fashioned technology, their evolution into micro and nano scales has unlocked new possibilities in the fields of robotics and AI, offering a level of precision, flexibility, and efficiency that traditional systems simply can’t match.
This article explores how miniature gears are poised to revolutionize robotics and AI, delving into their unique advantages, applications, and the innovations they bring to the table.
The Rise of Miniature Gears: A New Era in Precision
At the core of many machines—whether mechanical, digital, or hybrid—are gears. Gears are fundamental components in converting rotational motion, transmitting power, and adjusting speed ratios. Traditionally, gears have been used in large, mechanical systems, from automobiles to factory machines. However, as technology advances, the need for smaller, more efficient components has spurred the development of miniature gears, which are increasingly being used in compact, high-precision applications.
Miniature gears are typically defined as gears with a diameter of less than 1 millimeter. They are often crafted with precision engineering techniques, such as micro-machining or micro-molding, and can be made from a variety of materials, including metals, polymers, and ceramics. These tiny gears offer remarkable advantages, including higher precision, lower energy consumption, and the ability to fit into smaller, more intricate designs.
The rise of miniature gears is part of a broader trend in robotics and AI toward miniaturization and flexibility. As robots and AI systems become more integrated into our daily lives, they need to be smaller, more agile, and more efficient. Miniature gears make this possible by enabling the creation of lightweight, highly functional machines capable of performing tasks that were once deemed too complex or impossible.
Applications in Robotics: Smaller, Smarter Machines
Robotics is one of the most promising fields for the application of miniature gears. Robots are used in a wide range of industries, from manufacturing to healthcare, logistics, and even space exploration. The need for precision, efficiency, and versatility has driven the demand for smaller components like miniature gears, which offer several key benefits:
1. Micro-Robots for Surgery and Medical Applications
One of the most exciting applications of miniature gears is in the development of medical micro-robots, particularly for minimally invasive surgeries. These robots require highly precise movements and the ability to operate within confined spaces. Miniature gears make it possible for these robots to perform delicate tasks with incredible accuracy.
For example, in minimally invasive surgeries, where traditional robotic arms are too large to navigate the body’s internal cavities, miniature gears enable micro-robots to perform tasks such as tissue removal, suturing, or even targeted drug delivery. These robots can navigate narrow blood vessels or internal organs, performing complex procedures with minimal damage to surrounding tissues. The compact size and precision of the gears used in these robots are essential for their functionality.

2. Swarming Robots: Efficiency Through Coordination
In environments where multiple robots need to work together, such as warehouses or agricultural fields, miniature gears play a crucial role in the coordination of movements. Swarming robots, which work together to complete tasks such as sorting, picking, or planting, rely on miniature gears to facilitate their synchronized actions.
The small size of these gears allows for highly efficient power transmission between robots, ensuring that they can move together without draining excessive energy. Furthermore, miniature gears enable these robots to maintain precision in their movements, which is essential for tasks like picking fragile objects or placing items in tight spaces. As AI algorithms improve, miniature gears help robots work together more seamlessly, contributing to the overall efficiency of the system.
3. Drone Technology: Stability and Precision
Miniature gears are also making waves in drone technology. Drones require highly stable, precise movements to navigate their environments and perform tasks like aerial surveillance, inspection, or delivery. In many drone systems, miniature gears are used to drive motors, control flight mechanisms, and adjust the positioning of cameras or sensors.
By integrating miniature gears into drone systems, manufacturers can reduce the size and weight of the drones while maintaining the necessary power and precision. This not only improves the drone’s performance but also allows for longer flight times and better battery efficiency. As drone technology continues to evolve, miniature gears will be essential for achieving higher levels of performance and versatility.
AI and Miniature Gears: Bridging the Gap Between the Digital and Physical Worlds
Artificial intelligence has seen exponential growth in recent years, with applications in fields as diverse as natural language processing, computer vision, and autonomous vehicles. However, one area where AI faces challenges is in its ability to interact with the physical world. AI systems often struggle to translate digital data into real-world actions, especially when precise movements are required. This is where miniature gears come into play.

1. Precision Control in AI Systems
In AI applications where precise, fine-tuned control is essential, miniature gears offer a solution. AI systems that require mechanical actuation—whether in robots, prosthetics, or automated manufacturing processes—rely on miniature gears to provide the fine control needed for accurate movements.
For example, prosthetic limbs, powered by AI algorithms, require miniature gears to control the movements of fingers, hands, and joints. These gears enable the prosthetic to mimic the natural movements of a human limb, offering a level of dexterity and flexibility that was previously unattainable. The AI algorithms in the prosthetic can adjust the gear movements in real-time based on feedback from sensors, allowing the user to perform tasks like grasping, lifting, or manipulating objects with incredible precision.
2. Miniature Gears in AI-driven Sensory Devices
Another exciting application of miniature gears is in the creation of AI-powered sensory devices. These devices, such as vision systems or tactile sensors, rely on miniature gears to adjust the position of lenses, mirrors, or probes to focus on objects of interest.
In AI systems for medical diagnostics, for example, miniature gears enable the movement of imaging devices, ensuring that they can focus on specific areas of the body with high accuracy. These gears allow AI systems to adjust the positioning of sensors in real-time, improving the quality of the data collected and enhancing the AI’s ability to make decisions based on that data.
3. AI and Automated Manufacturing
Automated manufacturing processes are another area where miniature gears are transforming AI applications. In modern factories, AI systems control machines that produce everything from electronics to automotive parts. These machines rely on miniature gears to perform precise movements and adjustments, ensuring that production lines run smoothly and efficiently.
The ability to integrate miniature gears into AI-controlled machines allows manufacturers to produce smaller, more complex products with greater precision. It also enables the automation of tasks that would have been too difficult or costly to perform with traditional machinery. As AI continues to advance, miniature gears will play a crucial role in pushing the boundaries of automated manufacturing.
The Future of Miniature Gears in Robotics and AI
The potential of miniature gears in robotics and AI is vast, and as technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking innovations. Advances in materials science, fabrication techniques, and AI algorithms will likely lead to even smaller, more efficient miniature gears, enabling the development of new applications in fields like space exploration, environmental monitoring, and human-computer interaction.
In space exploration, for instance, miniature gears could be used in the design of robots that can explore the surfaces of other planets or moons. These robots would need to operate in extreme environments, where size and weight are critical factors. Miniature gears could allow these robots to perform complex tasks, such as collecting samples, taking measurements, or assembling structures, while using minimal power and maintaining high precision.
Similarly, miniature gears could enable the development of AI systems for environmental monitoring, where robots are used to monitor air quality, track wildlife, or detect pollution. These robots would need to be small enough to navigate complex ecosystems, but powerful enough to gather valuable data.
Conclusion: A Small Revolution with Big Impact
Miniature gears may be small, but their impact on robotics and AI is immense. By enabling more precise, efficient, and compact machines, these tiny components are helping to drive the next wave of innovation in both fields. From medical robots to swarming drones, miniature gears are playing a pivotal role in the development of new technologies that will transform industries, improve quality of life, and shape the future of artificial intelligence.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that miniature gears are more than just a tool—they are a key enabler of a new generation of smarter, more capable robots and AI systems. Their versatility, precision, and power efficiency make them a cornerstone of the ongoing revolution in robotics and AI. In this small, seemingly simple technology lies the potential to revolutionize how we live, work, and interact with machines.