In the ever-evolving world of digital art, trends shift as quickly as technology itself. Among the most intriguing developments in the field of digital illustration is the rise of hyperrealism. For many, the term evokes images of photorealistic portraits and mind-bending visual effects that blur the line between art and reality. But is hyperrealism just another fleeting trend, or does it signify a new, enduring movement in the digital arts?
In this article, we’ll explore the growing prominence of hyperrealism in digital illustration, its technical and creative nuances, and how it stands out in the crowded landscape of digital art. We will also touch on its potential to influence future trends and artists’ workflows, while considering how this style aligns with or challenges the broader evolution of digital media.
What is Hyperrealism?
At its core, hyperrealism refers to a genre of art that seeks to create images that are so incredibly detailed and lifelike that they often surpass ordinary photographic representations. It’s an artistic approach that focuses on the minutiae—the tiny details that most observers would overlook but which give life to the representation.
While hyperrealism has roots in traditional media, particularly drawing and painting, its modern interpretation is now increasingly associated with digital tools. In the digital realm, hyperrealism is achieved through powerful software like Adobe Photoshop, Corel Painter, and various 3D modeling programs. These tools enable artists to create highly detailed, pixel-perfect works that often appear indistinguishable from photographs.
Why is Hyperrealism Gaining Popularity?
The surge in digital hyperrealism can be attributed to several factors. First, technological advancements in hardware and software have made it easier for artists to replicate reality with precision. Graphics tablets like the Wacom Cintiq, alongside powerful digital painting applications, offer unprecedented control, enabling artists to mimic traditional techniques—such as blending, shading, and texture—digitally.
Second, hyperrealism satisfies the growing demand for high-definition, visually arresting artwork. As online platforms and social media increasingly rely on eye-catching visuals to engage audiences, hyperrealistic images stand out. They capture attention, evoke emotion, and create memorable visual experiences.
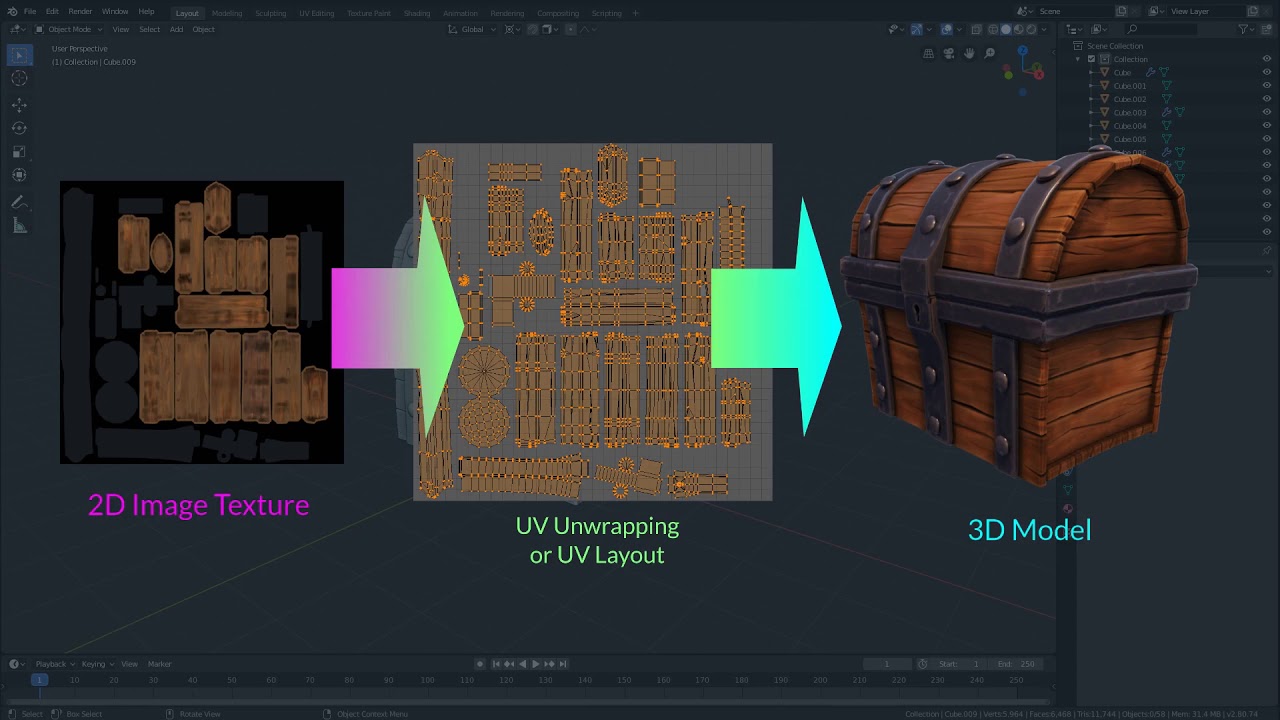
Finally, the trend of hyperrealism reflects a broader cultural fascination with technology and its relationship to reality. In a time where virtual and augmented realities are becoming more prevalent, hyperrealism can be seen as a reflection of our collective desire to explore, replicate, and even surpass the real world. Artists are using digital mediums not only to represent life as it is but to push the boundaries of what reality itself can look like.
The Technical Side of Digital Hyperrealism
Creating hyperrealistic digital illustrations is no small feat. It involves intricate techniques that demand both artistic talent and technical skill. Artists must have a deep understanding of light, texture, color theory, and perspective to accurately replicate reality. Here’s a look at some of the key techniques involved:
1. Layering and Blending
Hyperrealistic digital works often require multiple layers to capture complex textures and details. Each element—whether it’s skin, hair, fabric, or metal—has to be painted in separate layers so that artists can refine each section without affecting the others. Digital tools allow for precise blending, which is critical for creating smooth transitions between shadows and highlights.
2. Custom Brushes
Artists use custom brushes in digital painting software to replicate the texture of real-world materials. For example, brushes that imitate the softness of skin or the sheen of glass can add an additional level of realism. These brushes are essential for capturing the subtleties of natural light and texture.
3. High-Resolution Work
Hyperrealism requires working at extremely high resolutions. Every tiny detail needs to be visible and sharp, whether it’s the pores on a person’s face or the individual fibers of a fabric. Artists often work in large canvases to ensure that they can zoom in and focus on minute aspects without losing clarity.
4. Lighting and Shadows
The play of light and shadow is one of the most important aspects of hyperrealism. In digital illustration, artists simulate natural and artificial light sources to create depth and dimension. By accurately depicting how light interacts with surfaces, they can create the illusion of three-dimensionality on a two-dimensional plane.
5. Photo Reference and Texture Mapping
To achieve lifelike accuracy, artists often rely on photographic references and texture mapping. These references are used to capture the minute details of skin, hair, water droplets, and other surfaces. Texture mapping, on the other hand, involves applying images or patterns to 3D models to replicate surface details that might be difficult to draw by hand.
How Hyperrealism Stands Out in the Digital Art Landscape
While digital illustration has always been a dynamic and diverse field, hyperrealism’s stark attention to detail sets it apart from other trends. In recent years, other styles such as flat design, minimalism, and abstract art have dominated digital illustration. These styles often prioritize simplicity and symbolic representation over lifelike detail.
Hyperrealism, however, stands in contrast to these movements, embracing complexity and precision. The labor-intensive nature of hyperrealistic artwork requires a deep commitment to craftsmanship, which may explain why it appeals to certain audiences who appreciate fine detail, authenticity, and visual awe.
Moreover, hyperrealism challenges digital artists to push beyond their tools and workflows to achieve something closer to real-world perfection. Artists working in hyperrealism must develop unique problem-solving skills to render lifelike representations of the world while still harnessing the flexibility that digital tools offer.
Hyperrealism’s Place in Contemporary Digital Media

Hyperrealism is more than just a trend in digital illustration—it’s an emerging style that speaks to broader shifts in how art is consumed and appreciated in the digital age. As content creators, advertisers, and media companies strive to capture the attention of ever-more-distracted audiences, hyperrealism’s visceral impact is becoming more valuable than ever. It’s no longer just about creating images; it’s about creating experiences that immerse and captivate the viewer.
The rise of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) has further fueled interest in hyperrealism. With the integration of digital art into these immersive environments, hyperrealistic art is being used to create hyperrealistic landscapes, characters, and even entire worlds. This opens up new possibilities for artists to explore the boundaries between the real and the imagined.
Furthermore, hyperrealism is influencing other forms of digital art, such as concept art for film, game design, and advertising, where visuals often need to evoke a sense of realism while still fitting into fictional or stylized contexts. Hyperrealistic images are particularly useful in cinematic trailers or promotional materials, where the goal is to make an immediate, impactful statement.
The Future of Hyperrealism in Digital Art
As technology continues to advance, it’s clear that hyperrealism in digital illustration is not a passing trend. In fact, it is likely to evolve further. One key area of development is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to assist in the creation of hyperrealistic images. AI-powered tools can help streamline the process of creating intricate details by automating repetitive tasks like shading or texture mapping, allowing artists to focus on more creative aspects of their work.
Additionally, 3D rendering software and real-time engines, such as Unreal Engine and Unity, are pushing the boundaries of hyperrealism even further. These platforms allow artists to create immersive 3D environments with photorealistic textures, lighting, and animation.
Challenges and Criticism
Despite its appeal, hyperrealism is not without its detractors. Some critics argue that it lacks the emotional depth or conceptual meaning found in other art styles. They contend that the obsession with technical perfection might overshadow the artistic message or narrative of a piece.
Furthermore, hyperrealism can be time-consuming and labor-intensive, which makes it a challenging style for many artists to sustain on a commercial scale. For digital illustrators, this means that while the style can be highly lucrative in specific markets, it also demands a level of commitment and expertise that is not always practical for every project.
Conclusion
Hyperrealism is much more than a temporary digital art trend. As technology advances and digital tools become more powerful, the potential for hyperrealistic art grows exponentially. The demand for lifelike, attention-grabbing visuals in industries like advertising, gaming, and entertainment continues to drive this trend forward. While there are challenges and criticisms to consider, the appeal of hyperrealism’s detail, depth, and immersive qualities cannot be denied. Whether you see it as an artistic revolution or a technical marvel, there’s no question that hyperrealism is shaping the future of digital illustration.